✅ Last Update: Mar 16, 2025 @ 7:10 am
New Zealand stands as a jewel in the southwestern Pacific Ocean.
Yet, a curious question often arises: What continent is New Zealand in?
- In this article, we will go through on a journey to unravel the geographical enigma of New Zealand’s continental identity.
1. Considering Zealandia
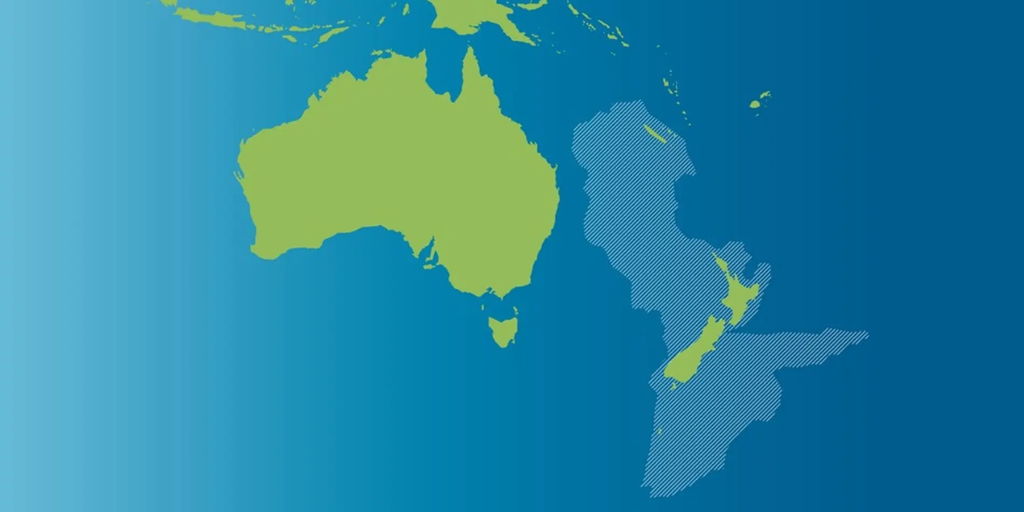
New Zealand’s continental identity gets more interesting when you look at Zealandia—a mostly submerged landmass that includes New Zealand and New Caledonia.
Zealandia challenges the usual idea of continents, with its elevated terrain, unique geology, and clear separation from the ocean floor. While not officially a continent, it suggests New Zealand is part of a much larger hidden landmass, reshaping how we think about Earth’s geology.
2. Australia and the Oceania Perspective
New Zealand is part of Oceania, a region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia.
While Australia is its closest neighbor, New Zealand is not part of the Australian continent. Instead, it has strong cultural ties to Polynesia and a distinct identity within the Pacific.
- This classification reflects New Zealand’s geopolitical and cultural connections with other Pacific nations.
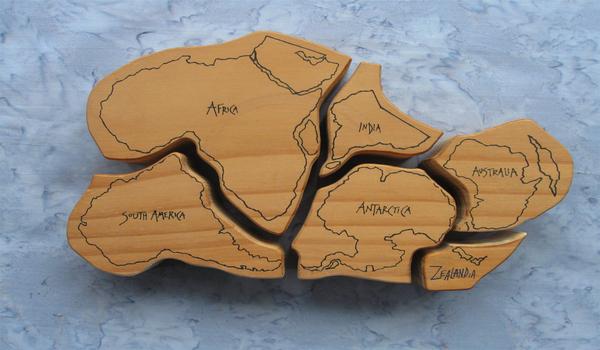
3. Understanding Geographic Continents
Before we dive into which continent New Zealand belongs to, let’s first clarify what a continent actually is.
Typically, continents are large, continuous landmasses surrounded by water.
The seven continents most people recognize are Africa, Antarctica, Asia, Europe, North America, Australia, and South America. But defining continents isn’t just about size and physical separation—it also involves history, culture, and geology.

4. Continental Plates and Tectonics
The Earth’s outer shell, called the lithosphere, is made up of rigid slabs known as tectonic plates. These plates float on a softer, semi-liquid layer beneath them, called the asthenosphere.
As they move and collide, they shape the planet—causing earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and even forming mountains.
- New Zealand sits right on the meeting point of the Indo-Australian and Pacific plates, making it a hotspot for geological activity.
5. New Zealand's Tectonic Landscape
New Zealand’s distinctive landscape is shaped by the tectonic forces in the region.
The country sits right on the boundary between two massive tectonic plates: the Indo-Australian Plate to the northwest and the Pacific Plate to the southeast.
When these plates collide, they create the Southern Alps, a mountain range that stretches along the South Island.
Meanwhile, the North Island is known for its volcanic activity, with famous cones like Mount Ruapehu and Mount Taranaki serving as reminders of the country’s fiery geological history.

6. Quick Facts about Zealandia (New Zealand)
🗺️ Zealandia: The Hidden Continent
Zealandia is a vast submerged landmass in the southwest Pacific, covering 4.9 million square kilometers, including parts of New Caledonia.
🏞️ Distinctive Geology
With its elevated land and separation from oceanic crust, Zealandia stands out as a unique geological feature.
🔍 Scientific Exploration
Scientists are using advanced sonar and mapping tech to explore Zealandia’s tectonic history and evolution.
🌋 Tectonic Activity
Zealandia sits at the boundary of the Indo-Australian and Pacific plates, part of the seismic Pacific Ring of Fire.
🌏 Implications for Geology
Recognizing Zealandia as a continent challenges our understanding of how landmasses are categorized.
🔬 Scientific Significance
Zealandia offers insights into continental evolution, tectonic interactions, and underwater geological formations.
🌐 Global Relevance
It’s a key area of research in plate tectonics, helping scientists understand Earth’s geological past.
📜 Historical Context
The idea of Zealandia has been around for a while, but new tech has brought it to the forefront of geological research.
🌊 Climate Change Link
Zealandia’s history is tied to past climate changes and sea level shifts, offering clues about Earth’s environmental changes.
🌍 Redefining Boundaries
Zealandia challenges the idea of fixed continental boundaries, showcasing Earth’s dynamic surface.
🌊 Marine Life and Oceanography
Its surrounding waters are rich in marine biodiversity, important for conservation efforts.
💡 Educational Value
Studying Zealandia sparks curiosity about Earth’s geology and hidden wonders beneath the ocean.
🌊 Conservation Efforts
As research continues, preserving Zealandia’s delicate ecosystems is a key consideration.
🔭 Future Research
Ongoing exploration may include drilling into the seabed to learn more about Zealandia’s history.